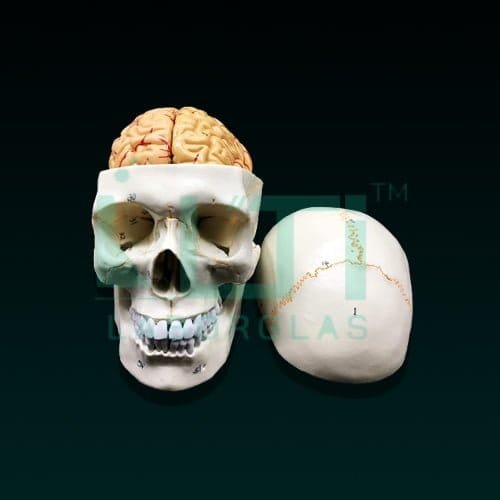
- Life size.
- Made of PVC.
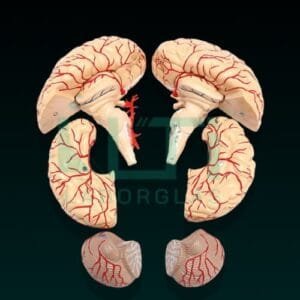
- Dissectable in 3 parts and brain in 8 parts.
- Brain model sits nicely inside the skull and can also be removed. The brain comes apart into the following pieces: Frontal and parietal lobes (2 parts), temporal and occipital lobes (2 parts), brain stem (2 parts) and cerebellum (2 parts).
- Both the brain and skull are held together with magnets and small pegs.
- Bonnet can be removed, mandible is movable, teeth are separately installed & all skull foramens, fissures, processes are well depicted.
- 32 features marked.
- Key card/ manual provided.
A human skull model with a numbered brain serves educational, medical, and research purposes by providing a detailed representation of the skull with labeled brain regions. Here’s a brief overview of its uses:
- Anatomy Education: Used for teaching anatomy, allowing students to study the skull and the numbered regions of the brain, enhancing understanding of neuroanatomy.
- Neuroscience Education: Beneficial for neuroscience education, illustrating the skull and specific brain areas with corresponding numbers for in-depth study.
- Medical Training: Supports medical training programs by providing an integrated model for studying the skull and understanding the localization of different brain regions.
- Patient Education: Enables healthcare practitioners to visually explain the relationship between the skull and brain regions, facilitating patient understanding of neurological conditions.
- Neurosurgery Planning: Healthcare professionals may use this model for surgical planning, emphasizing the spatial relationships between the skull and brain structures.
- Psychology Studies: Relevant in psychology studies to understand the physical connections between the skull and brain regions, contributing to discussions on behavior and cognition.
- Research Reference: Provides researchers with an accurate model for studying the anatomy and localization of specific brain areas, contributing to neuroscience research.
- Educational Displays: Used in educational displays at museums, health fairs, and other events to showcase the intricacies of the skull and brain anatomy.