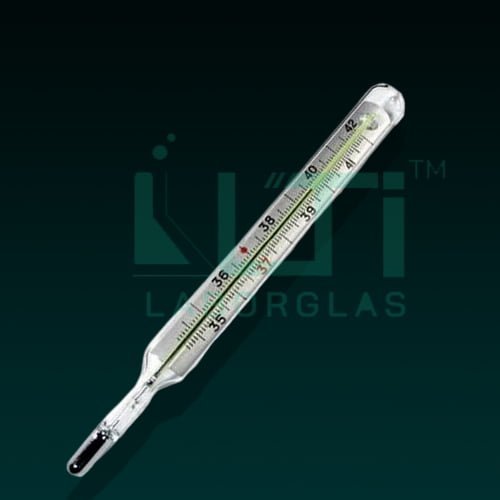
- Permanent fused scale, with constriction in bore to prevent mercury from going back, in case.
| Part No. | Description |
| 9300 | THERMOMETER CLINICAL |
Here are some common clinical uses of thermometers:
- Body Temperature Measurement: The primary use of clinical thermometers is to measure body temperature. This is crucial for detecting fever, one of the common symptoms of various illnesses, infections, or other health conditions.
- Diagnostic Tool: Elevated body temperature, or fever, can be an important diagnostic indicator. Measuring temperature helps healthcare professionals assess the severity of an illness and determine appropriate treatment strategies.
- Monitoring Health Conditions: Regular temperature monitoring is essential for individuals with certain health conditions, such as infections, chronic diseases, or compromised immune systems. Changes in body temperature can indicate the progression or resolution of an illness.
- Screening for Infectious Diseases: In some situations, such as during disease outbreaks, temperature screening is conducted as a preliminary measure to identify individuals with fever, which may be a symptom of infectious diseases.
- Post-Surgery Monitoring: After surgery, monitoring body temperature is important to detect and prevent complications such as infections. An elevated temperature may indicate an inflammatory response.
- Pediatric Care: Clinical thermometers are commonly used for monitoring the health of infants and children. Specialized thermometers, such as tympanic (ear) or temporal artery thermometers, are often used for non-invasive and quick temperature measurements in children.
- Home Health Monitoring: Many people use clinical thermometers at home to monitor their temperature during periods of illness. This allows for prompt medical attention if a fever is detected.
- Temperature Charting: In certain medical conditions, such as fertility tracking or hormonal therapies, individuals may use basal body temperature charts to monitor subtle changes in body temperature over time.