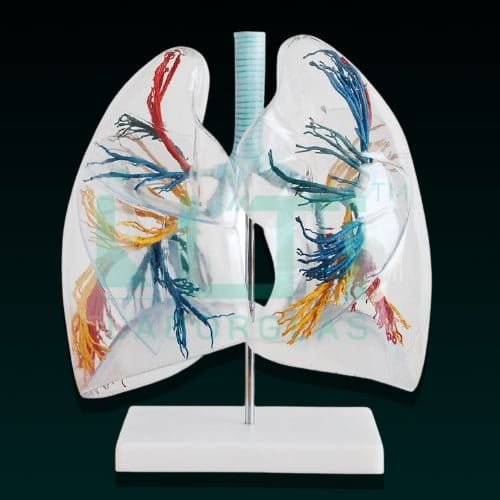
- Presents 10 segments in the right lung and 8 in the left . the distributions of the bronchial tree can be observed through the transparent lungs.
- Right lung: right upper lobe (3 segments), right middle lobe (2 segments), right inferior lobe (5 segments)
- Left lung: left upper lobe (4 segments), left inferior lobe (4 segments).
- Distribution of the bronchial tree: right bronchus, left bronchus.
- Hilus of lung, the lung made of transparent plastic. The trachea and bronchial tree is made of PVC
A model of the transparent lung segment serves educational, medical, and research purposes, providing a detailed representation of a clear or transparent lung section. Here’s a brief overview of its uses:
- Respiratory Physiology Education: Used for teaching respiratory physiology, allowing students to study the structures and functions of the lungs in detail.
- Pulmonology Training: Beneficial for pulmonology education, illustrating the anatomy of the lungs for in-depth study and understanding.
- Patient Education: Enables healthcare practitioners to visually explain respiratory conditions, diseases, and treatment options to patients using a transparent lung model.
- Respiratory Therapy Training: Relevant in respiratory therapy education for understanding lung anatomy and the dynamics of respiratory function.
- Research Reference: Used in research settings to study lung pathology, respiratory diseases, and the impact of various conditions on lung structures.
- Medical Imaging Interpretation: Practical for enhancing the interpretation skills of medical imaging professionals by providing a tangible representation of lung anatomy.
- Simulation Training: Useful for simulating respiratory scenarios, allowing healthcare professionals to practice procedures and interventions on a clear lung model.
- Public Health Education: Displayed in educational exhibits to enhance public understanding of respiratory health and lung anatomy.